The most bright US dam-removal effort to this level has begun
At the help of the dam —
As US dams age, removal is consistently an possibility—and it could per chance per chance be done nicely.
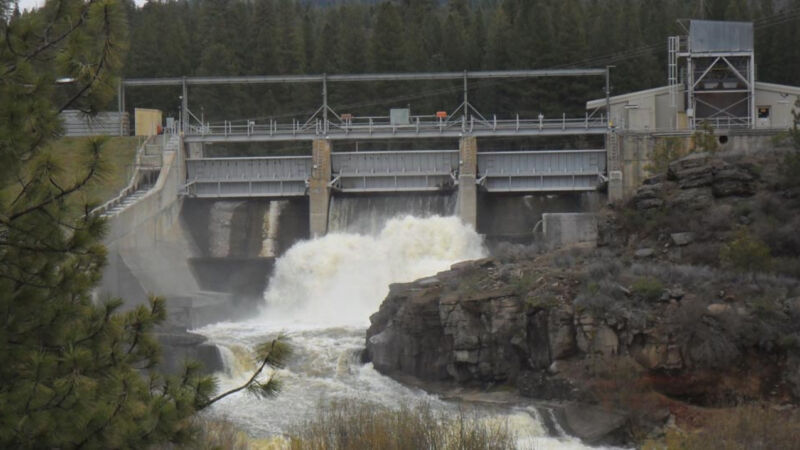

Amplify / The John C. Boyle Dam, in actual fact one of many dams slated for removal.
Wending its procedure from the Olympic Mountains to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, Washington’s Elwha River is now free. For approximately century, the Elwha and Gilnes Canyon Dams corralled these waters. Both beget since been eliminated, and the restoration of the watershed has began.
The dam-removal challenge used to be one of the important bright to this level in the US—even though it received’t capture that region for lengthy. The Klamath River dam removal challenge has begun, with four of its six dams—J.C. Boyle, Copco No. 1, Copco No. 2, and Iron Gate—plot to be scuppered by the discontinuance of the year, and the drawdown began this week. (If fact be told, Copco No. 2 is already long previous.)
Once the challenge is total, the Klamath will bustle from Oregon to northwestern California largely unimpeded, allowing sediment, natural topic, and its restive waters to waft freely downriver whereas fish indulge in salmon, trout, and replace migratory species leap and wriggle their procedure upstream to spawn.
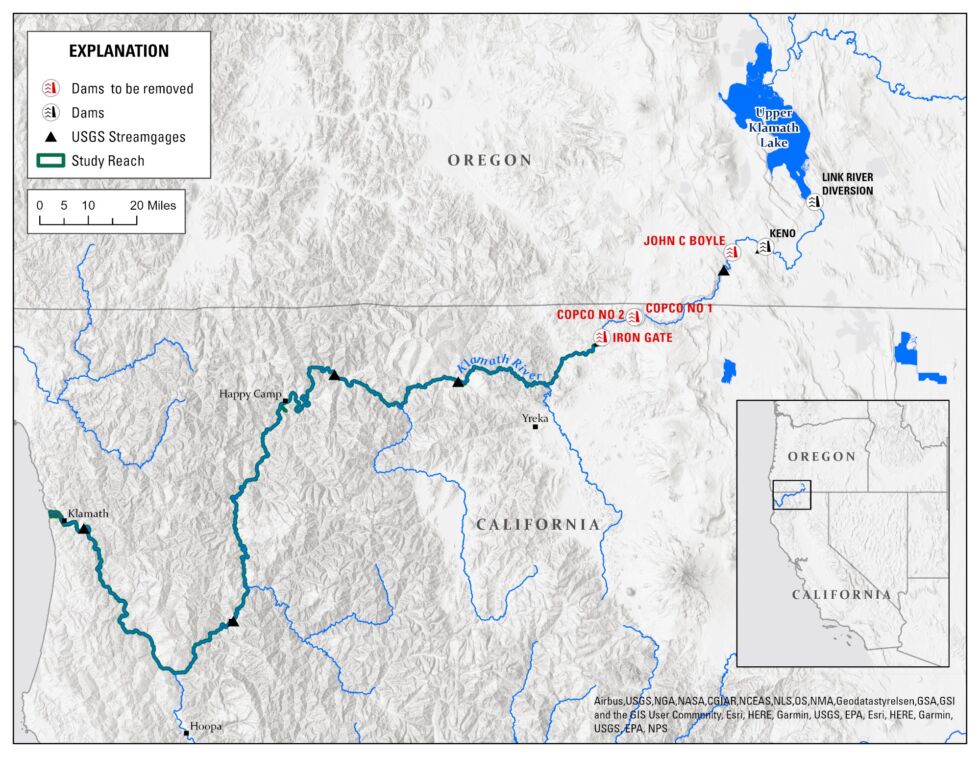
Amplify / Draw exhibiting the positioning of the Klamath River Basin, with the four dams plot to be eliminated proven in red.
Across the US, dams are being eliminated for replace reasons. Many are merely long-established. “They’re in rivers beyond their designated existence span,” acknowledged Lucy Andrews, a doctoral pupil at the College of California, Berkeley, who stories water resource administration. “They beget got a high doable of failure, particularly when local weather commerce is taken into account.” In replace words, these dams weren’t designed for at the present time’s capricious precipitation regimes. Other dams now no longer feature in the manner they were designed, acknowledged Jonathan Warrick, a coastal geomorphologist with the US Geological Stare.
Removal can additionally reverse ecological bother that, in the western US, most incessantly harms migratory fish but can additionally motive complications for more than a few mute species and ecosystems. As well, dams “beget displaced tribal international locations from their lands and severed connections to culturally important waterways and species,” Andrews acknowledged, talking particularly about California. “In these contexts, dam removal can in actuality be an important step in direction of repair.”
Taming the water
Dams, each and every orderly and miniature, help replace purposes, acknowledged Andrews (orderly dams are largely these taller than 15 meters—roughly the high of a four-yarn building).
“Many dams were constructed in the jap states for mills and energy generation,” acknowledged Warrick. Numerous these dams were slightly miniature, but after World Battle II, orderly dams proliferated across the West. This day, US dams control floods, generate hydroelectric energy, and retailer water for municipal or agricultural train, he defined. “Most dams are built to create quite of bit of every and every.” Game additionally components into price-profit analyses for existing dams, Warrick acknowledged.
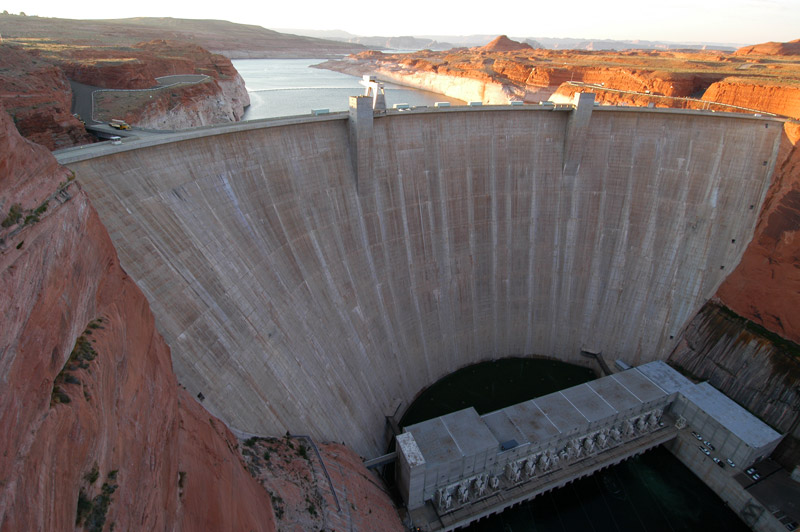

The Glen Canyon dam impounds the Colorado River in northern Arizona and is amongst the elevated of the “orderly” dams in the US, with a high of 220 meters (710 feet).
Nonetheless “dams disrupt a ramification of things thru the river corridor,” Warrick acknowledged. “Dams prefer any sediment that is flowing downstream.”
Because the upstream river empties into the reservoir, it loses energy, which governs its ability to capture sediment. A delta of sand and gravel propagates at the upstream facet of the lake that kinds in the help of a dam—far away from the dam itself. Glorious and muddy sediment could per chance per chance drape the relaxation of the reservoir. In some conditions, the reservoir fills fully with sediment, turning the dam into waterfall, as has came about at Southern California’s Rindge Dam. (For the time being, there are ways you are going to rating sediment out of reservoirs, ranging from dredging and hauling to building sediment bypass tunnels that train gravity and the river itself to create the work.)
-
Where the Colorado River enters Lake Mead, a delta is being formed.
-
The Rindge Dam stoppers Malibu Creek and its sediment in the Santa Monica Mountains of Southern California.