X-chromosome inactivation would possibly well merely decrease autism risk, search for in mice suggests
A search for in mice suggests how chromosome inactivation would possibly well merely supply protection to ladies from a make of autism disorder inherited from their father’s X chromosome.
Females inherit two copies of the X chromosome, one from their mother and one from their father. Because cells create now not want two copies, the cells inactivate one reproduction early in embryonic constructing, a neatly-studied process identified as X chromosome inactivation.
As a results of this inactivation, each female is made up of a combination of cells, some like an active X chromosome from her father and others from her mother, a phenomenon identified as mosaicism.
For plenty of years, it has been knowing that this turned into random and would end result, on reasonable, in a roughly 50/50 combination of cells, with 50% having an active paternal X chromosome and 50% having an active maternal X chromosome.
Now a original search for finds that, within the mouse mind no now not as a lot as, that is now not the case. In its attach, there seems to be a bias within the process that finally ends up within the paternal X chromosome being inactivated in 60% of the cells in preference to the anticipated 50%.
When the X-linked mutation that’s basically the most customary motive of autism spectrum disorder is inherited from the father, the sample of X-chromosome inactivation within the mind circuitry of females can prevent the results of that mutation, the quest for learned.
“This bias would possibly well be one device to decrease the risk of inferior mutations, which happen extra incessantly in male chromosomes,” mentioned Eric Szelenyi, performing assistant professor of biological structure on the University of Washington College of Medications in Seattle. He’s the corresponding creator of a paper describing the findings within the journal Cell Reports. Dr. Pavel Osten, an adjunct professor at Chilly Spring Harbor Laboratory in Fresh York, turned into the paper’s senior creator.
The X-chromosome is of particular passion since it carries extra genes alive to about mind constructing than every other chromosome. Mutations within the chromosome are linked to extra than 130 neurodevelopmental disorders, including fragile X syndrome and autism.
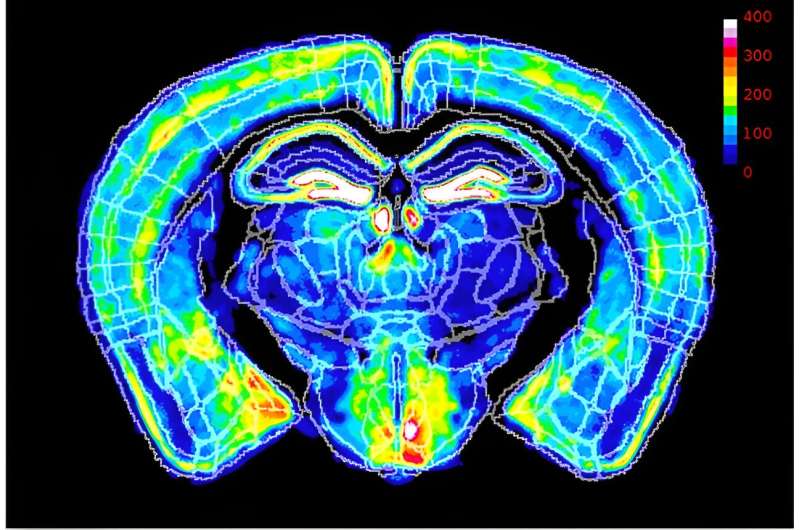
Within the quest for, the researchers first certain the ratio of X chromosome inactivation in healthy mice by analyzing roughly 40 million mind cells per mouse. The scientists did this by the utilization of excessive-throughput volumetric imaging and computerized counting. This prognosis revealed a scientific 60: 40 ratio at some point of all conceivable anatomical areas.
They then examined what would happen within the event that they presented a inferior mutation into the X chromosomes. The mutation they frail turned into a mouse mannequin for fragile X syndrome. This syndrome is mainly the most customary make of inherited intellectual and developmental disability in humans.
They first examined the mice for behaviors regarded as analogous to those impaired in other folks with fragile X syndrome. These tests evaluate such issues as their sensorimotor characteristic, spatial memory and traits against fright and sociability.
They stumbled on that the mice who inherited the mutation on their mother’s X chromosome, which are much less doubtless to be inactivated within the 60: 40 ratio, were extra doubtless to display habits analogous to fragile X syndrome. They exhibited extra signs of fright, much less sociability, awful efficiency in spatial discovering out, and deficits in sensorimotor characteristic.
But mice that inherited the mutation from one of their father’s X chromosomes, which were extra doubtless to be inactivated, didn’t seem impaired.
“What turned into most tantalizing is that the utilization of every animal’s behavioral efficiency turned into most accurately predicted by X chromosome inactivation in mind circuits, in preference to just having a peek on the mind as a total, or single mind areas,” mentioned Szelenyi. “This implies that having extra mutant X-active cells due to maternal inheritance will enhance total illness risk, nonetheless particular mosaic sample within mind circuitry within the close decides which behaviors are impacted basically the most.”
“This implies that the 20% distinction in mutant X-active cells created by the bias would possibly well merely moreover be protective against X mutations from the father, which happen extra customarily,” he mentioned.
The findings would possibly well merely moreover display why symptoms of X-linked syndromes, like X-linked autism spectrum disorder, fluctuate extra in females than males.
Extra records:
Eric R. Szelenyi et al, Dispensed X chromosome inactivation in mind circuitry is expounded with X-linked illness penetrance of habits, Cell Reports (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114068
Citation:
X-chromosome inactivation would possibly well merely decrease autism risk, search for in mice suggests (2024, April 30)
retrieved 30 April 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/records/2024-04-chromosome-inactivation-autism-mice.html
This document is subject to copyright. Except for any just dealing for the aim of personal search for or evaluate, no
fragment would possibly well be reproduced with out the written permission. The teach material is provided for records capabilities most tantalizing.