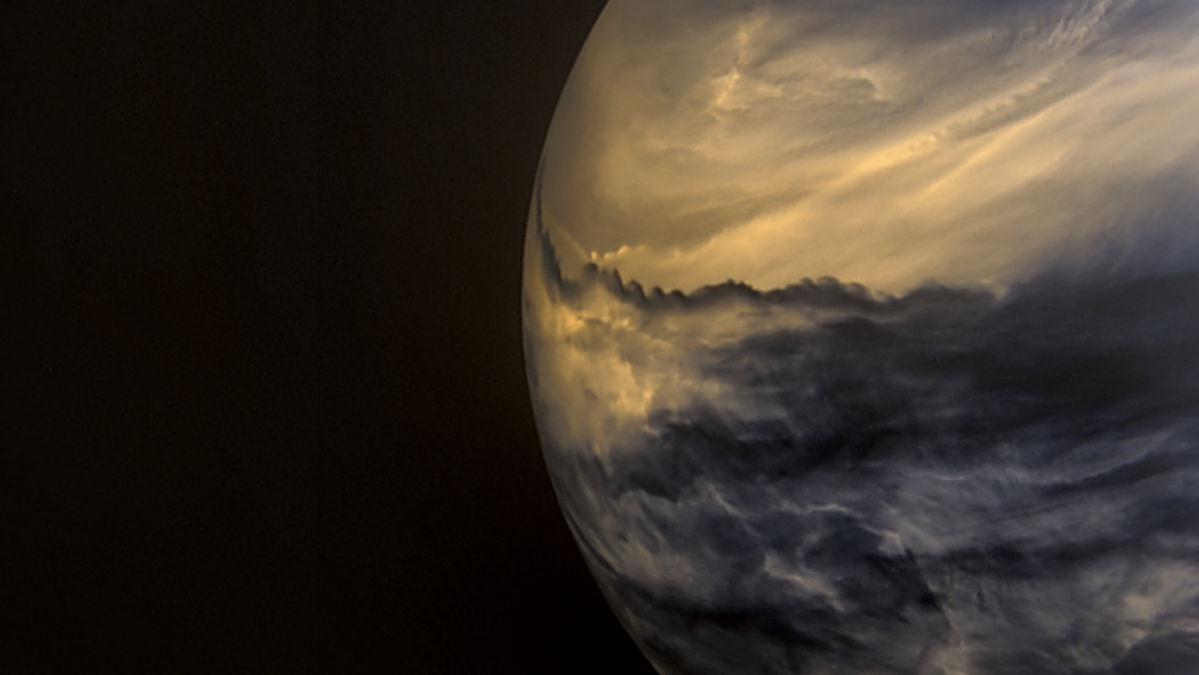
Venus wasnt consistently hell, scientists mutter. It will possess had beaches.

Venus as considered in infrared gentle by the Japanese Akatsuki spacecraft.
Credit: AXA / ISAS / DARTS / Damia Bouic
It is that you just are going to be ready to imagine that Venus and Earth as soon as simultaneously existed as gratifying worlds net hosting cushy temperatures and oceans.
Then, one thing went awry.
In new study, planetary scientists simulated how Venusian stipulations at the moment time — with pizza oven-delight in temperatures, a crushing ambiance, and former evidence of frequent volcanism — got right here to be. The outcomes recommend that Venus, over a series of huge volcanic outgassing events and different geologic changes, transitioned from an Earth-delight in world to the hellish land we peep at the moment time. Even the longest-lived robotic despatched to Venus survived for real two hours.
“It is hot sufficient to soften lead,” Matthew Weller, a planetary geophysicist at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute who coauthored the new study, told Mashable. “It is miles a truly noxious self-discipline to be.”
The hunt for has been published within the undercover agent-reviewed journal Science Advances.
Venus and Earth, though they’ve taken two dramatically different climatic roads, are regarded as sibling planets. They’re about the a similar dimension. They’re made out of the a similar rocky stuff. They both dwell within the internal fragment of the solar system. So what came about?
“You are going to need these two planets sitting there, after which one spins off in a single other course,” Weller defined.
Mashable Light Tempo
We are in a position to now not, needless to scream, hotfoot aid in time to accumulate out why. Nor can we ship geologists there to sleuth the Venusian previous. Nevertheless the researchers mature superior computer simulations — which created 3D spherical fashions of geologic assignment on Venus— of how the new rock convecting beneath the outside, known as the mantle, broke Venus’ crust and finally drove the merciless outcomes contemporary at the moment time. “Venus on the total baked itself,” Weller said.
“Venus on the total baked itself.”
Working the fashions showed that a as soon as temperate, Earth-delight in Venus skilled a series of “stairstep” events, whereby deep interior motions rupturing the crust allowed for volcanism to attain Venus’ surface. This ended in molten rock resurfacing the planet and big volcanic outgassing to trust the ambiance, rising large surface stress. Over extra than one durations of some 60 million years, every outgassing episode will possess added three to 10 times extra atmospheres (an ambiance, or atm, is a unit of stress representing one ambiance on Earth) to Venus’ ambiance. This day, the stress on the Venusian surface is 92 bars, or 1,350 psi. “To position this into context, imagine having 1,350 kilos (over 600 kilograms) resting on one sq. hump of your body; it’d be delight in having a little car sitting for your thumbnail,” the Planetary Society explains.

A conceptual illustration exhibiting astronomical oceans on Venus lengthy ago.
Credit: NASA

Venus as considered from NASA’s Mariner 10 spacecraft in 1974.
Credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech
It is unknown when, precisely, these planet-altering events started. It will possess been loads of billion years ago, or great extra “now not too lengthy ago” at heaps of of thousands and thousands of years ago. Nevertheless, for many eons, both Earth and Venus will possess hosted astronomical oceans and balmy temperatures, with water rippling onto shorelines. And they’d possess been real some 67 million miles other than every different (a minute cosmic distance).
“It is that you just are going to be ready to imagine both had been habitable,” Weller said.
Importantly, the Venus-Earth dichotomy unearths how great a planet can replace. An exoplanet we peep at the moment time, many gentle-years away in deep location, would possibly possibly be aware totally different within the discontinuance. Or Earth, with out being pummeled by a astronomical asteroid, would possibly possibly markedly transform, too. “Planets replace dramatically over time,” Weller emphasised. “It reveals how straightforward it is for an Earth-delight in planet to grow to be delight in Venus.”
“It reveals how straightforward it is for an Earth-delight in planet to grow to be delight in Venus.”
The “million-dollar search info from,” nonetheless, is what to begin with pushed Venus onto this trajectory of repeated episodes of coarse volcanism, surface rupturing, and prodigious outgassing. It will possess been an extremely large eruptive tournament at the spoiled time that fed into a runaway cycle. Geologically, a world’s ambiance and internal-workings are inextricably linked, as stipulations within the ambiance influence what transpires beneath a planet’s surface. For instance, on Earth, rock weathering, over heaps of of thousands and thousands of years, removes warmth-trapping carbon dioxide from the air, appearing to stabilize the native climate. On Venus, dramatically cranking up surface temperature can abolish plate tectonics, Weller defined, shutting off a planet’s ability to stabilize itself.
This can possess pushed Venus to veer sharply from its Earthly environs. And since the researchers simulated, it can well now not turn around.
Within the impending years, Venus would possibly possibly grow great less mystifying. A NASA mission known as DAVINCI — immediate for Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging — will drop a three-foot-large titanium sphere thru Venus’ thick clouds. Over the course of real an hour, the probe will ingest gases, walk experiments, and mutter us what Venusian mountains in fact be aware delight in. This is in a position to well dramatically toughen our belief of Venus, and why it be so now not like its rocky “twin,” Earth.

Establish is an award-successful journalist and the science editor at Mashable. After working as a ranger with the National Park Service, he started a reporting profession after seeing the extraordinary price in instructing other folk about the happenings on Earth, and former.
He is descended 2,500 feet into the ocean depths making an strive for the sixgill shark, ventured into the halls of high R&D laboratories, and interviewed some of the most attention-grabbing scientists on the planet.
Probabilities are you’ll well presumably attain Establish at [email protected].
These newsletters would possibly possibly possess promoting, affords, or affiliate links. By clicking Subscribe, you verify you are 16+ and conform to our Terms of Expend and Privateness Protection.